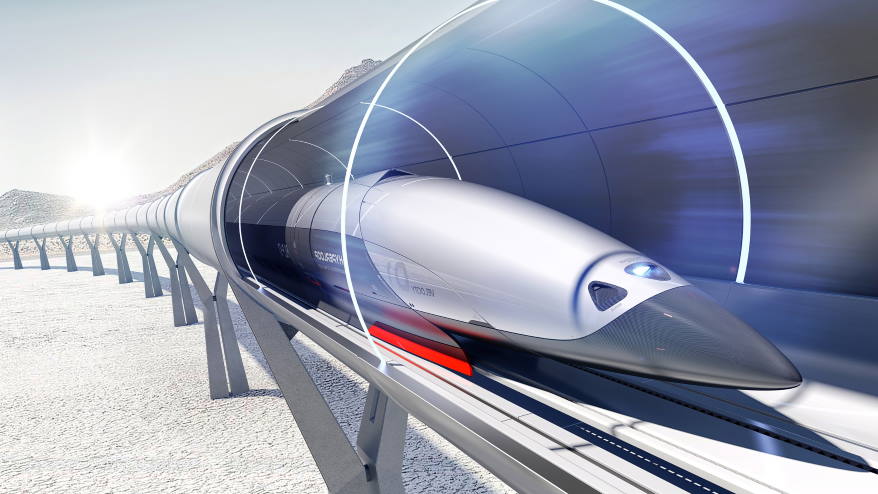
Hyperloop is a new form of ground transportation presently in development by a number of companies. It might see guests taking a trip at over 700 miles an hour in drifting pod which races along within huge low-pressure tubes, either above or listed below ground. Is Hyperloop faster than a plane?
What makes Hyperloop different?
There are 2 huge distinctions in between Hyperloop and standard rail. The pods bring travelers take a trip through tubes or tunnels from which most of the air has been removed to decrease friction. This must permit the pods to take a trip at approximately 750 miles per hour.
Rather than utilizing wheels like a train or car, the pods are created to drift on air skis, utilizing the same standard concept as an air hockey table, or use magnetic levitation to minimize friction.
What are the advantages of Hyperloop?
Advocates argue that Hyperloop might be less expensive and faster than train or car travel, and less expensive and less contaminating than flight. They declare that it’s also quicker and more affordable to construct than standard high-speed rail.
Hyperloop might for that reason be used to take the load off the roads, making travel in between cities much easier, and possibly unlocking significant financial advantages as an outcome.
Information about Hyperloop speed vs plane speed and rail speed
Fans argue that Hyperloop is substantially much better than high-speed rail. It is lower expense and more energy effective because, to name a few things, the track does not need to offer power to the pods constantly and, as the pods can go every thirty seconds. It’s also possibly 2 or 3 times faster than even high-speed rail.
What’s next for Hyperloop?
Hyperloop is a technology that, for its fans a minimum of, might have a huge effect. It might lower flight in between huge cities, increase economies and trade, and minimize the pressure on housing in cities by enabling commuters to live even more away.
There are significant technical and business difficulties that Hyperloop innovations will need to prevail over before they can bring travelers in convenience through a pneumatic tube, not to mention change the world.
The next phase for Hyperloop is to move beyond preliminary testing and expediency studies, begin longer distance trials of the technology and, a lot more significantly, testing the service with travelers.